Can Dialated Arteries Become Narrow Again
High blood pressure (hypertension) is persistently high pressure in the arteries.
-
Often no cause for loftier blood force per unit area tin can be identified, but sometimes it occurs as a issue of an underlying disorder of the kidneys or a hormonal disorder.
-
Obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, stress, smoking, and excessive amounts of booze or sodium (salt) in the nutrition all can play a role in the development of high blood pressure in people who have an inherited trend to develop it.
-
In virtually people, high blood force per unit area causes no symptoms.
-
Doctors make the diagnosis after measuring blood pressure on two or more occasions.
-
People are advised to lose weight, end smoking, and decrease the amounts of sodium and fats in their nutrition.
-
Antihypertensive drugs are given.
To many people, the give-and-take hypertension suggests excessive tension, nervousness, or stress. In medical terms, hypertension refers to persistently high blood force per unit area, regardless of the crusade. Because it usually does not crusade symptoms for many years—until a vital organ is damaged—high blood pressure has been called the silent killer. Uncontrolled high blood pressure increases the adventure of problems such as stroke Overview of Stroke A stroke occurs when an artery to the brain becomes blocked or ruptures, resulting in decease of an area of brain tissue due to loss of its claret supply (cerebral infarction) and symptoms that... read more , aneurysm Overview of Aortic Aneurysms and Aortic Dissection The aorta, which is about 1 inch (ii.5 centimeters) in diameter, is the largest artery of the body. It receives oxygen-rich claret from the left ventricle and distributes it to all of the body... read more than , heart failure Heart Failure (HF) Centre failure is a disorder in which the eye is unable to keep up with the demands of the body, leading to reduced blood period, back-upwards (congestion) of blood in the veins and lungs, and/or... read more  , heart set on Overview of Coronary Artery Illness (CAD) Coronary artery disease is a condition in which the blood supply to the middle musculus is partially or completely blocked. The heart muscle needs a constant supply of oxygen-rich claret. The coronary... read more than
, heart set on Overview of Coronary Artery Illness (CAD) Coronary artery disease is a condition in which the blood supply to the middle musculus is partially or completely blocked. The heart muscle needs a constant supply of oxygen-rich claret. The coronary... read more than  , and chronic kidney disease Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic kidney disease is a slowly progressive (months to years) decline in the kidneys' power to filter metabolic waste products from the blood. Major causes are diabetes and loftier blood pressure level... read more .
, and chronic kidney disease Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic kidney disease is a slowly progressive (months to years) decline in the kidneys' power to filter metabolic waste products from the blood. Major causes are diabetes and loftier blood pressure level... read more .
Almost 75 one thousand thousand Americans are estimated to have high blood force per unit area. High blood pressure occurs more often in blacks—in 41% of black adults compared with 28% of whites and 28% of Mexican Americans. It too occurs with high frequency in people whose ancestors are from China, Japan, and other Eastward Asian or Pacific areas (such as Koreans,Thais, Polynesians, Micronesians, Filipinos, and Maori). The consequences of loftier blood pressure level are worse for blacks and those of Asian descent. High blood pressure occurs more often in older people—in most two thirds of people anile 65 or older, compared with simply nigh one 4th of people aged 20 to 74. People who have normal blood pressure at historic period 55 accept a 90% risk of developing high claret pressure at some point in their life. High blood force per unit area is twice equally common among people who are obese as among those who are not.
In the The states, only an estimated 81% of people with high blood pressure have been diagnosed. Of people with a diagnosis of high claret force per unit area, about 73% receive handling, and of the people receiving treatment, well-nigh 51% take adequately controlled claret pressure level.
When blood pressure is checked, two values are recorded. The higher value reflects the highest pressure level in the arteries, which is reached when the centre contracts (during systole). The lower value reflects the lowest pressure level in the arteries, which is reached just earlier the heart begins to contract over again (during diastole). Blood pressure is written as systolic pressure/diastolic pressure—for example, 120/80 mm Hg (millimeters of mercury). This reading is referred to as "120 over 80."
Blood pressure in adults is classified as normal, elevated blood pressure, stage one (mild) hypertension, or stage 2 hypertension.
However, the higher the claret pressure level, the greater the risk of complications—even inside the normal blood pressure range—so these limits are somewhat capricious.
A hypertensive urgency is diastolic blood pressure level that is more than than 120 mm Hg but has not nonetheless caused whatever organ damage that is apparent to people or their doctors. A hypertensive urgency ordinarily does not cause symptoms.
A hypertensive emergency is a especially severe form of high blood pressure level. Diastolic blood pressure is at least 120 mm Hg, and in that location is evidence of progressive damage in 1 or more vital organs (typically the brain, heart, and kidneys), often accompanied by a multifariousness of symptoms. Hypertensive emergencies are uncommon, merely they are several times more than common among blacks than among whites, amidst men than among women, and among people in lower socioeconomic groups than among those in college socioeconomic groups. If untreated, a hypertensive emergency tin exist fatal.
The torso has many mechanisms to control blood pressure. The body tin alter the
-
Corporeality of blood the eye pumps
-
Diameter of arteries
-
Volume of claret in the bloodstream
To increase blood pressure, the heart tin can pump more than blood past pumping more forcefully or more rapidly. Small-scale arteries (arterioles) can narrow (tuck), forcing the claret from each heartbeat through a narrower infinite than normal. Because the infinite in the arteries is narrower, the aforementioned corporeality of claret passing through them increases the blood pressure. Veins tin can tuck to reduce their capacity to agree blood, forcing more than claret into the arteries. As a result, claret pressure increases. Fluid can be added to the bloodstream to increment blood volume and thus increment blood force per unit area.
To subtract claret pressure, the center tin can pump less forcefully or rapidly, arterioles and veins can widen (dilate), and fluid can be removed from the bloodstream.
-
The sympathetic sectionalization stimulates the adrenal glands to release the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). These hormones stimulate the middle to trounce faster and more forcefully, most arterioles to tuck, and some arterioles to amplify. The arterioles that dilate are those in areas where an increased blood supply is needed (such as in skeletal muscle—the muscles controlled by conscious effort).
-
The sympathetic division as well stimulates the kidneys to decrease their excretion of sodium and water, thereby increasing blood volume. The body controls the movement of sodium in and out of cells, to prevent an excess of sodium within cells. Excessive amounts of sodium inside cells tin can cause the body to become overly sensitive to stimulation by the sympathetic division.
The kidneys as well respond direct to changes in blood pressure. If blood pressure level increases, the kidneys increase their excretion of sodium and water, and then that blood book decreases and claret pressure returns to normal. Conversely, if blood pressure decreases, the kidneys decrease their excretion of sodium and water, so that blood volume increases and blood pressure level returns to normal. The kidneys tin increase blood pressure by secreting the enzyme renin, which somewhen results in the production of the hormone angiotensin Ii.
Angiotensin II helps increment claret pressure by
-
Causing the arterioles to tuck
-
Triggering the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous arrangement
-
Triggering the release of two other hormones, aldosterone and vasopressin (as well called antidiuretic hormone), which cause the kidneys to increase the retention of sodium and water
The kidneys normally produce substances that cause arterioles within the kidney to dilate. This helps balance the effects of hormones that cause constriction of arterioles.
Blood pressure varies naturally over a person's life. Infants and children normally accept much lower blood pressure level than adults. For most everyone living in industrialized countries such as the Usa, blood pressure increases with aging. Systolic pressure increases until at to the lowest degree age lxxx, and diastolic pressure level increases until age 55 to 60, so levels off or even decreases. However, for people living in some developing countries, neither systolic nor diastolic pressure level increases with aging, and high blood force per unit area is practically nonexistent, maybe because sodium intake is low and the concrete activity level is higher.
Regulating Claret Pressure: The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a series of reactions designed to assistance regulate blood pressure.
-
When claret pressure falls (for systolic, to 100 mm Hg or lower), the kidneys release the enzyme renin into the bloodstream.
-
Renin splits angiotensinogen, a large poly peptide that circulates in the bloodstream, into pieces. One slice is angiotensin I.
-
Angiotensin I, which is relatively inactive, is dissever into pieces by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). I piece is angiotensin II, a hormone, which is very active.
-
Angiotensin Two causes the muscular walls of minor arteries (arterioles) to constrict, increasing claret force per unit area. Angiotensin II too triggers the release of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands and vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) from the pituitary gland.
-
Aldosterone and vasopressin cause the kidneys to retain sodium (table salt). Aldosterone likewise causes the kidneys to excrete potassium. The increased sodium causes water to exist retained, thus increasing blood volume and blood pressure.
Activeness temporarily affects claret pressure, which is higher when a person is active and lower when a person rests. Blood pressure also varies with the fourth dimension of day: It is highest in the morning time and lowest at night during sleep. These variations are normal. Whenever a change causes a transient increase in blood pressure, one of the torso's compensatory mechanisms is triggered to counteract the change and go along blood pressure level at normal levels. For instance, an increase in the amount of blood pumped out past the heart—which tends to increase claret force per unit area—causes dilation of blood vessels and an increase in the kidneys' excretion of sodium and h2o—which tend to reduce claret pressure.
Loftier blood pressure may be
-
Primary
-
Secondary
High claret pressure with no known cause is called main (formerly called essential) hypertension. Between 85% and 95% of people with high blood pressure have main hypertension. Several changes in the center and blood vessels probably combine to increment blood pressure level. For instance, the corporeality of blood pumped per minute (cardiac output) may exist increased, and the resistance to blood menstruation may be increased because blood vessels are constricted. Blood volume may be increased also. The reasons for such changes are not fully understood simply appear to involve an inherited abnormality affecting the constriction of arterioles, which help command blood pressure. Other changes may contribute to increases in blood pressure, including accumulation of excessive amounts of sodium inside cells and decreased product of substances that dilate arterioles.
High claret pressure with a known cause is called secondary hypertension. Between five% and 15% of people with high blood pressure have secondary hypertension.
In many of these people, high claret pressure results from
-
A kidney disorder
Many kidney disorders tin cause high blood pressure level because the kidneys are of import in controlling blood pressure. For instance, damage to the kidneys resulting from inflammation or other disorders may impair their ability to remove enough sodium and water from the body, increasing claret volume and blood pressure. Other kidney disorders that cause loftier blood pressure include renal artery stenosis Blockage of the Renal Arteries Gradual narrowing (stenosis) or sudden, complete blockage (occlusion) may touch arteries that supply the right or the left kidney, their branches, or a combination. Kidney failure or loftier blood... read more (narrowing of the artery supplying 1 of the kidneys), which may be due to atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a status in which patchy deposits of fat material (atheromas or atherosclerotic plaques) develop in the walls of medium-sized and large arteries, leading to reduced or... read more 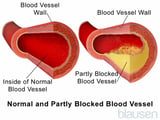 , kidney infection Kidney Infection Pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection of one or both kidneys. Infection can spread up the urinary tract to the kidneys, or uncommonly the kidneys may become infected through bacteria in the... read more (pyelonephritis), glomerulonephritis Glomerulonephritis Glomerulonephritis is a disorder of glomeruli (clusters of microscopic blood vessels in the kidneys with small-scale pores through which claret is filtered). It is characterized by body tissue swelling... read more , kidney tumors Kidney Cancer About solid kidney tumors are cancerous, but purely fluid-filled tumors (cysts) generally are not. Almost all kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma. Another kind of kidney cancer, Wilms tumor... read more than , polycystic kidney disease Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Polycystic kidney disease is a hereditary disorder in which many fluid-filled sacs (cysts) form in both kidneys. The kidneys grow larger just have less performance tissue. Polycystic kidney disease... read more , injury to a kidney, and radiation therapy affecting a kidney.
, kidney infection Kidney Infection Pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection of one or both kidneys. Infection can spread up the urinary tract to the kidneys, or uncommonly the kidneys may become infected through bacteria in the... read more (pyelonephritis), glomerulonephritis Glomerulonephritis Glomerulonephritis is a disorder of glomeruli (clusters of microscopic blood vessels in the kidneys with small-scale pores through which claret is filtered). It is characterized by body tissue swelling... read more , kidney tumors Kidney Cancer About solid kidney tumors are cancerous, but purely fluid-filled tumors (cysts) generally are not. Almost all kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma. Another kind of kidney cancer, Wilms tumor... read more than , polycystic kidney disease Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Polycystic kidney disease is a hereditary disorder in which many fluid-filled sacs (cysts) form in both kidneys. The kidneys grow larger just have less performance tissue. Polycystic kidney disease... read more , injury to a kidney, and radiation therapy affecting a kidney.
In a few people, secondary hypertension is caused by some other disorder, such as
-
Hormonal disorders
-
Use of sure drugs
Hormonal disorders that cause high claret pressure include hyperaldosteronism Hyperaldosteronism In hyperaldosteronism, overproduction of aldosterone leads to fluid retention and increased blood pressure, weakness, and, rarely, periods of paralysis. Hyperaldosteronism tin can be caused by a... read more than (overproduction of aldosterone, oftentimes past a noncancerous tumor in one of the adrenal glands), Cushing syndrome Cushing Syndrome In Cushing syndrome, the level of corticosteroids is excessive, usually due to taking corticosteroid drugs or overproduction by the adrenal glands. Cushing syndrome usually results from taking... read more  (a disorder characterized by high levels of cortisol), hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism is overactivity of the thyroid gland that leads to high levels of thyroid hormones and speeding up of vital body functions. Graves affliction is the well-nigh common cause of hyperthyroidism... read more
(a disorder characterized by high levels of cortisol), hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism is overactivity of the thyroid gland that leads to high levels of thyroid hormones and speeding up of vital body functions. Graves affliction is the well-nigh common cause of hyperthyroidism... read more  (an overactive thyroid gland), and, rarely, a pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma A pheochromocytoma is a tumor that commonly originates from the adrenal glands' chromaffin cells, causing overproduction of catecholamines, powerful hormones that induce high claret force per unit area and... read more (a tumor that is located in an adrenal gland and that produces the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine ).
(an overactive thyroid gland), and, rarely, a pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma A pheochromocytoma is a tumor that commonly originates from the adrenal glands' chromaffin cells, causing overproduction of catecholamines, powerful hormones that induce high claret force per unit area and... read more (a tumor that is located in an adrenal gland and that produces the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine ).
Drugs that tin can crusade or worsen high blood pressure include booze (excessive use), cocaine, corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), oral contraceptives (nativity command pills), and sympathomimetics (certain decongestants in cold remedies, such every bit pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine).
Stress tends to crusade claret pressure level to increase temporarily, but blood pressure level usually returns to normal once the stress is over. An example is "white coat hypertension," in which the stress of visiting a md's function causes blood pressure to increase plenty to exist diagnosed as high claret pressure in someone who has normal claret pressure at other times. People with "white coat hypertension" seem to have a slightly higher chance of developing permanent loftier blood pressure level, but they probably do non need treatment unless their blood pressure is very high in the office.
In near people, high blood pressure causes no symptoms, despite the coincidental occurrence of certain symptoms that are widely, but erroneously, attributed to high blood pressure level: headaches, nosebleeds, dizziness, a flushed face, and fatigue. People with high blood pressure may take these symptoms, but the symptoms occur just every bit frequently in people with normal claret pressure.
Severe or long-continuing loftier blood force per unit area that is untreated can crusade symptoms considering it can impairment the brain, eyes, centre, and kidneys. Symptoms include headache, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, and restlessness. Occasionally, severe high blood pressure causes the encephalon to swell, resulting in nausea, vomiting, worsening headache, drowsiness, confusion, seizures, sleepiness, and fifty-fifty blackout. This condition is called hypertensive encephalopathy.
Astringent high claret pressure level increases the workload of the heart and may crusade breast pain and/or shortness of jiff. Sometimes very loftier claret pressure causes the big artery that carries blood from the heart (the aorta) to tear, causing chest or abdominal hurting. People who accept such symptoms accept hypertensive emergencies and, equally such, require emergency treatment.
If high claret pressure is due to a pheochromocytoma, symptoms may include severe headache, feet, an awareness of a rapid or irregular heart rate (palpitations), excessive perspiration, tremor, and paleness. These symptoms result from high levels of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine , which are secreted by the pheochromocytoma.
Long-standing high blood pressure tin can damage the centre and claret vessels and increment the take a chance of
-
Measuring blood pressure
For the most accurate readings, those that are used to diagnose someone with high blood pressure every bit opposed to a casual check, blood pressure must be measured following a specific procedure (see Measuring Claret Pressure level Measuring Blood Force per unit area  ). Blood pressure is measured later on a person sits for v minutes. The person must have had no exercise, caffeine, or smoking for at least 30 minutes earlier the measurement. A reading of 130/80 mm Hg or more is considered high, but a diagnosis cannot be based on a single high reading. Sometimes, even several high readings are not enough to make the diagnosis—because, for instance, the readings may vary too much. If a person has an initial high reading, blood force per unit area is measured again during the same visit and so measured twice on at least two other days to make sure that the high blood pressure is still nowadays.
). Blood pressure is measured later on a person sits for v minutes. The person must have had no exercise, caffeine, or smoking for at least 30 minutes earlier the measurement. A reading of 130/80 mm Hg or more is considered high, but a diagnosis cannot be based on a single high reading. Sometimes, even several high readings are not enough to make the diagnosis—because, for instance, the readings may vary too much. If a person has an initial high reading, blood force per unit area is measured again during the same visit and so measured twice on at least two other days to make sure that the high blood pressure is still nowadays.
Measuring Blood Pressure
Several instruments can measure blood force per unit area rapidly and with trivial discomfort. A sphygmomanometer is commonly used. It consists of a soft rubber gage connected to a safety seedling that is used to inflate the cuff and a meter that registers the pressure of the cuff. The meter may be a dial or a glass column filled with mercury. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) because the outset musical instrument used to measure it was a mercury column.
When a sphygmomanometer is used, a person sits with legs uncrossed and back supported. An arm is bared (if a sleeve is rolled up, caution is needed to ensure that it is non tight effectually the arm), bent, and resting on a tabular array, so that the arm is about the same level as the heart. The cuff is wrapped effectually the arm. Using a cuff that is proportional to the size of the arm is important. If the cuff is likewise minor, the claret force per unit area reading is too high. If the gage is too large, the reading is too low.
Listening with a stethoscope placed over the artery beneath the cuff, a health care practitioner inflates the cuff past squeezing the bulb until the gage compresses the artery tightly plenty to temporarily stop blood flow, unremarkably to a pressure level that is nigh 30 mm Hg college than the person's usual systolic pressure (the pressure exerted when the centre beats). So the gage is gradually deflated. The pressure at which the practitioner first hears a pulse in the avenue is the systolic pressure. The cuff continues to exist deflated, and at some point, the audio of blood flowing stops. The pressure at this signal is the diastolic pressure (the pressure exerted when the heart relaxes, betwixt beats).
Some instruments tin measure blood pressure automatically, without use of a stethoscope or rubber seedling. These devices may fit around the upper arm, finger, or wrist. For people older than 50, claret pressure measured at the upper arm is the near authentic. Sometimes a precise measurement of blood pressure is needed—for case, for a person in an intensive care unit. In such cases, a catheter can be inserted inside an artery to measure blood pressure directly.
Instruments to measure blood pressure are available for domicile use past people who have loftier blood pressure.
If there is still uncertainty, a 24-hr blood pressure level monitor may be used. Information technology is a portable battery-operated device, worn on the hip, connected to a claret pressure cuff, worn on the arm. This monitor repeatedly records blood pressure throughout the day and night over a 24-hour or 48-hour period. The readings decide not but whether high blood pressure is present but also how severe it is.
Pseudohypertension, blood force per unit area that is measured as high when it is non, occurs in people with very strong arteries (most ordinarily, in older people). It occurs when the artery in the arm is too strong to be compressed by the blood force per unit area cuff, and as a issue, blood pressure cannot be measured accurately.
Masked hypertension occurs when blood pressure is measured as normal when it is high. Masked hypertension affects up to 10% of people who have high blood pressure level. Recognizing this blazon of high blood pressure level may be impossible unless blood pressure is measured at dwelling or if a complexity (for case, heart failure) is suspected to accept been acquired by loftier blood pressure level.
After high claret force per unit area has been diagnosed, its effects on central organs, especially the blood vessels, heart, brain, eyes, and kidneys, are usually evaluated. Doctors besides await for the crusade of loftier claret pressure. The number and blazon of tests that are done to expect for organ damage and to determine the cause of high blood pressure vary from person to person. In general, routine evaluation for all people with high blood force per unit area involves a medical history Medical History and Physical Examination for Heart and Blood Vessel Disorders The medical history and concrete examination tin can suggest that a person has a middle or blood vessel disorder that requires additional testing for accurate diagnosis. When doctors "accept a medical... read more than  , a physical examination Medical History and Physical Test for Heart and Blood Vessel Disorders The medical history and concrete test can propose that a person has a heart or blood vessel disorder that requires additional testing for accurate diagnosis. When doctors "have a medical... read more
, a physical examination Medical History and Physical Test for Heart and Blood Vessel Disorders The medical history and concrete test can propose that a person has a heart or blood vessel disorder that requires additional testing for accurate diagnosis. When doctors "have a medical... read more  , electrocardiography Electrocardiography Electrocardiography (ECG) is a quick, simple, painless procedure in which the middle's electrical impulses are amplified and recorded. This record, the electrocardiogram (as well known as an ECG)... read more
, electrocardiography Electrocardiography Electrocardiography (ECG) is a quick, simple, painless procedure in which the middle's electrical impulses are amplified and recorded. This record, the electrocardiogram (as well known as an ECG)... read more 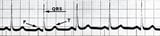 (ECG), blood tests (including the hematocrit level [the portion of total blood volume made up of red blood cells], potassium and sodium levels, and tests of kidney role Kidney Function Tests Doctors tin can assess kidney function by doing tests on blood and urine samples. Creatinine, a waste production, is increased in the blood when kidney part is decreased by a large amount. Creatinine... read more ), and urine tests.
(ECG), blood tests (including the hematocrit level [the portion of total blood volume made up of red blood cells], potassium and sodium levels, and tests of kidney role Kidney Function Tests Doctors tin can assess kidney function by doing tests on blood and urine samples. Creatinine, a waste production, is increased in the blood when kidney part is decreased by a large amount. Creatinine... read more ), and urine tests.
The physical exam includes checking the expanse of the abdomen over the kidneys for tenderness and placing a stethoscope over the abdomen to listen for a bruit (the sound acquired by claret rushing through a narrowed avenue) in the artery supplying each kidney.
A stethoscope is used to detect heart sounds. An abnormal heart sound, called the quaternary middle sound, is ane of the earliest changes in the heart caused by high claret pressure level. This sound develops because the left atrium of the heart has to contract harder to fill the enlarged, potent left ventricle, which pumps blood to all of the body except the lungs.
Kidney impairment can be detected past urine and blood tests. Urine tests can observe early evidence of kidney harm. The presence of blood cells and albumin (the most arable protein in blood) in the urine may betoken such damage. Symptoms of kidney damage (such as languor, poor appetite, and fatigue) practice not unremarkably develop until 70 to 80% of kidney part is lost.
The higher the blood pressure and the younger the person, the more extensive the search for a crusade is likely to be, fifty-fifty though a cause is identified in less than 10% of people. A more extensive evaluation may include 10-ray, ultrasonography, and radionuclide imaging of the kidneys and their blood supply as well as a breast ten-ray. Blood and urine tests are done to measure the levels of certain hormones, such equally epinephrine , aldosterone, and cortisol.
The cause may be suggested past abnormal results of a physical examination or past the symptoms. For example, a bruit in the avenue to a kidney may suggest renal artery stenosis Blockage of the Renal Arteries Gradual narrowing (stenosis) or sudden, consummate blockage (apoplexy) may bear upon arteries that supply the right or the left kidney, their branches, or a combination. Kidney failure or high claret... read more (narrowing of the artery supplying a kidney). Diverse combinations of symptoms may suggest high levels of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine produced past a pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma A pheochromocytoma is a tumor that commonly originates from the adrenal glands' chromaffin cells, causing overproduction of catecholamines, powerful hormones that induce loftier claret pressure and... read more . The presence of a pheochromocytoma is confirmed when the breakup products of these hormones are detected in the urine. Other rare causes of high blood pressure may be detected past certain routine tests. For example, measuring the potassium level in the claret can help detect hyperaldosteronism Hyperaldosteronism In hyperaldosteronism, overproduction of aldosterone leads to fluid retention and increased claret pressure level, weakness, and, rarely, periods of paralysis. Hyperaldosteronism tin can exist caused past a... read more .
-
Diet and exercise
-
Drugs to lower blood pressure
Primary hypertension cannot exist cured, only it tin be controlled to forbid complications. Anybody with elevated claret pressure or any stage of hypertension should change their lifestyle. The decision to prescribe drugs is based on the actual claret force per unit area level and whether people take atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or have a more than than 10% take chances of developing information technology in the next 10 years.
Doctors ofttimes recommend that people with loftier claret pressure monitor their own blood pressure at domicile. Self-monitoring probably helps motivate people to follow a dr.'south recommendations regarding treatment.
The goal for antihypertensive therapy is to decrease blood pressure to below 130/80 mm Hg in almost people. Still, if decreasing a person's claret pressure to less than 130/80 mm Hg causes problems, such as fainting, calorie-free headedness, retentivity loss, or dizziness, doctors may recommend a higher blood pressure level goal just not higher than 140/90. For some people, for example, those at high chance of eye affliction, a lower systolic goal may be appropriate.
Overweight people with high claret pressure are advised to lose weight. Losing as few as 10 pounds (4.v kilograms) can lower claret pressure. For people who are obese or who accept diabetes or high cholesterol levels, changes in diet (ane rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-fatty dairy products, with reduced saturated and total fat content) are important for reducing the risk of heart and blood vessel affliction.
Reducing the intake of booze and sodium (while maintaining an adequate intake of calcium, magnesium, and potassium) may make drug therapy for loftier blood pressure level unnecessary. Daily alcohol intake should be reduced to no more than 2 drinks (a daily total of 24 ounces [about ane liter] of beer, eight ounces [nigh 240 milliliters] of wine, or 2 ounces [nigh threescore milliliters] of 100-proof whiskey or other liquor) in men and ane drinkable in women. Daily sodium intake should be reduced to less than 2½ grams, or sodium chloride (common salt) intake, to six grams.
Drugs that are used in the handling of high blood pressure are chosen antihypertensives. With the wide variety of antihypertensives available, loftier claret force per unit area tin can exist controlled in about anyone, merely treatment has to be tailored to the individual. Handling is most constructive when the person and physician communicate well and interact on the treatment plan.
Different types of antihypertensives reduce blood force per unit area by different mechanisms, and then many unlike handling strategies are possible. For some people, doctors apply a stepped approach to drug therapy: They first with 1 type of antihypertensive and add others equally necessary. For other people, doctors find a sequential arroyo is preferable: They prescribe one antihypertensive, and if it is ineffective, they stop it and prescribe another type. For people with blood pressure at or higher up 140/ninety mm Hg, usually ii drugs are started at the same time. In choosing an antihypertensive, doctors consider such factors equally
-
The person's age, sex, and race
-
The severity of high blood pressure
-
The presence of other conditions, such as diabetes or high blood cholesterol levels
-
Potential side furnishings, which vary from drug to drug
-
The costs of the drugs and of tests needed to check for certain side effects
A majority of people (more than 74%) ultimately require two or more drugs to reach their claret pressure goal.
Most people tolerate their prescribed antihypertensive drugs without problems. But any antihypertensive drug tin can cause side effects. So if side effects develop, a person should tell the doctor, who can adjust the dose or substitute some other drug. Usually, an antihypertensive drug must be taken indefinitely to control blood pressure.
If people still take high blood pressure despite taking three different drugs, doctors in Europe sometimes insert a catheter into the artery to each kidney. The catheter produces radio waves that destroy the sympathetic nerves along the renal arteries. The offset studies on this process appeared to bear witness that it lowered blood force per unit area. Nevertheless, a much larger and more than complete report did not evidence that the procedure worked. This treatment is non available in the Us.
Some other treatment for high blood pressure level is called pacemaker therapy. An electrode is implanted in the cervix, where it stimulates certain nerve endings that assist regulate blood pressure. This treatment is not available in the The states, but it is available in Europe and Canada.
In hypertensive emergencies, claret force per unit area must exist lowered quickly. Hypertensive emergencies are treated in hospital intensive intendance units. Most drugs used to rapidly lower blood pressure level, such as fenoldopam, nitroprusside, nicardipine, or labetalol, are given intravenously.
Untreated high claret pressure increases a person's take a chance of developing heart illness (such equally heart failure, centre assault, or sudden cardiac expiry), kidney failure, or stroke at an early on age. High blood pressure is the virtually important adventure factor for stroke. It is also one of the three most of import run a risk factors for eye attack that a person can modify (the other two are smoking and high cholesterol levels in the claret).
Handling that lowers high blood pressure level greatly decreases the risk of stroke and heart failure. Such treatment may also decrease the risk of a heart assail, although not as dramatically.
The following is an English-linguistic communication resource that may be useful. Please note that THE Transmission is not responsible for the content of this resources.
-
American Heart Association: Loftier blood pressure: Comprehensive resource to help people understand causes of high blood pressure and manage the lifestyle changes required for treatment
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/heart-and-blood-vessel-disorders/high-blood-pressure/high-blood-pressure
0 Response to "Can Dialated Arteries Become Narrow Again"
إرسال تعليق